Aspartic Acid
Aspartic acid, also known as aspartic acid, is an alpha-amino acid. The L-isomer of aspartic acid is one of the 20 amino acids of the protein, the structural unit of 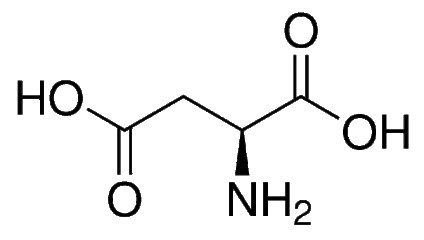 protein. Aspartic acid is ubiquitous in biosynthesis. White crystalline or crystalline powder, slightly acidic. Soluble in boiling water, slightly soluble in water (0.5%) at 25 ° C, soluble in dilute acid and sodium hydroxide solution, insoluble in ethanol, ether, heated to 270 ° C decomposition, isoelectric point 2.77 it can be used as K+, Mg2+ The ion carrier transports electrolytes to the myocardium, thereby improving myocardial contractile function, while reducing oxygen consumption, and protecting the myocardium in the absence of oxygen in coronary circulatory disorders. It participates in the ornithine cycle, promotes the production of urea by oxygen and carbon dioxide, reduces the amount of nitrogen and carbon dioxide in the blood, enhances liver function and eliminates fatigue.
protein. Aspartic acid is ubiquitous in biosynthesis. White crystalline or crystalline powder, slightly acidic. Soluble in boiling water, slightly soluble in water (0.5%) at 25 ° C, soluble in dilute acid and sodium hydroxide solution, insoluble in ethanol, ether, heated to 270 ° C decomposition, isoelectric point 2.77 it can be used as K+, Mg2+ The ion carrier transports electrolytes to the myocardium, thereby improving myocardial contractile function, while reducing oxygen consumption, and protecting the myocardium in the absence of oxygen in coronary circulatory disorders. It participates in the ornithine cycle, promotes the production of urea by oxygen and carbon dioxide, reduces the amount of nitrogen and carbon dioxide in the blood, enhances liver function and eliminates fatigue.
Benefits and Applications
1. As an electrolyte supplement for amino acid infusion, potassium, calcium and other inorganic ion supplements, fatigue recovery agents. Potassium magnesium aspartate injection or oral solution for arrhythmia caused by cardiac glycoside poisoning and premature beats, tachycardia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, heart failure, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, hepatitis, cirrhosis, etc. Disorders. It is a low-toxicity, this product can not be injected without dilution, and those with renal insufficiency and atrioventricular block should be used with caution.
2. It can be used as ammonia antidote, liver function accelerator, fatigue recovery agent and other pharmaceuticals. It can be used as an additive for L-ascorbate food additives and various refreshing beverages. It can also be used as a biochemical reagent, medium and organic synthesis. body.
3. For the synthesis of sweeteners, for the treatment of heart disease in medicine, as a liver function enhancer, ammonia antidote, fatigue elimination agent and amino acid infusion ingredients.
4. Nutritional supplements, sputum and flavoring agents. Add to a variety of refreshing drinks. It is used as an ammonia antidote, a liver function enhancer, and a fatigue recovery agent in medicine.
5. For biochemical research, used as fatigue recovery agent, ammonia antidote, clinical diagnostic drug.
Attentions
1. Liver disease causes liver damage, resulting in high aspartate aminotransferase. Common liver diseases that cause high aspartate aminotransferase are: acute and chronic hepatitis, fatty liver, alcoholic liver, cirrhosis or liver cancer.
2, heart disease causes heart damage, resulting in high aspartate aminotransferase. Common heart diseases that cause high aspartate aminotransferase are: myocarditis, myocardial infarction, and heart failure.
3, other diseases cause high aspartate aminotransferase, such as typhoid, pneumonia, nephritis, cholecystitis, gallstones, tuberculosis, infectious mononucleosis and other diseases.
In addition, strenuous exercise, taking drugs that are irritating to the liver, and excessive drinking can also cause high aspartate aminotransferase, and pregnant women will also cause aspartate aminotransferase.







Leave A Comment